Understanding the Multiple Nuclei Model of Cities
What is the Multiple Nuclei Model?
The Multiple Nuclei Model of cities with Artificial Intelligence, introduced by Chauncy Harris and Edward Ullman in 1945, suggests that urban areas develop around multiple centers or nuclei. Unlike traditional models that emphasize a single central business district (CBD), this model recognizes several distinct hubs within a city. Each nucleus serves a specific function, such as commercial, industrial, or residential purposes.
Importance of Understanding Urban Land Use Models
Grasping urban land use models like the Multiple Nuclei Model is essential for:
- Urban Planning: Helps planners design efficient and sustainable cities.
- Real Estate Investments: Assists investors in identifying high-growth areas, especially with the rise of Artificial Intelligence in Real Estate which is revolutionizing the property market by transforming every aspect of the buying, selling, and management process.
- Infrastructure Development: Guides the development of transportation and utility networks.
Understanding these models empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions that shape vibrant and functional urban environments.
Overview of Urbanization and Suburbanization Trends
Urbanization has surged globally, with more than half the world’s population now residing in cities. This shift prompts increased demand for housing, infrastructure, and services. Suburbanization, the process where people move from central urban areas to suburbs, has also gained momentum. This trend leads to the emergence of new nuclei outside traditional city centers, transforming urban geography.
By studying these trends through the lens of the Multiple Nuclei Model, we gain valuable insights into modern urban dynamics. Furthermore, understanding how market segmentation is revolutionizing real estate with AI can provide additional perspectives on these changes.
The Role of PropTech in Real Estate
The emergence of PropTech companies is another significant development in the real estate sector. These companies are leveraging innovative technology to transform the way we buy, sell, and manage properties. As these trends continue to evolve, tools like Fotocasa and HelloData are becoming increasingly important for maximizing real estate listings and gaining competitive advantages in this dynamic market.
Historical Context of Urban Models
Urban land use models have evolved significantly before the emergence of the Multiple Nuclei Model. Early frameworks sought to explain the spatial organization and growth of cities.
1. Concentric Zone Model
The Concentric Zone Model was developed by Ernest Burgess in 1925. This model depicts urban areas as a series of concentric rings emanating from a central business district (CBD). Key features include:
- The CBD at the center.
- Surrounding transitional zone with deteriorating housing, factories, and immigrant settlements.
- Working-class residential zones.
- Middle-class residential areas further out.
- Suburban commuter zones at the periphery.
2. Hoyt’s Sector Model
Introduced by Homer Hoyt in 1939, Hoyt’s Sector Model proposes that cities grow in sectors or wedges, not rings. Sectors radiate from the CBD along transportation routes like railroads and highways. Key features include:
- High-rent residential sectors developing outward from the CBD.
- Industrial sectors located along transport routes.
- Low-income housing situated near industrial zones.
The transition to the Multiple Nuclei Model marked a shift in understanding urban growth. Harris and Ullman introduced this model in 1945, recognizing cities could develop multiple centers or “nuclei” rather than a single core. These nuclei might include separate clusters for business, industry, and residential areas, each influencing urban structure independently.
This understanding is crucial when considering replacement reserves in real estate, which are essential for maintaining property value over time. The concept of stabilized value also plays a significant role in real estate investments, providing insights into long-term profitability.
Moreover, modern technology has revolutionized how we analyze these urban models and their implications on real estate. For instance, with advancements in AI, we now have tools that allow us to scrape real estate data more efficiently, leading to better decision-making processes.
Furthermore, understanding the differences between black box AI and explainable AI is vital for those looking to leverage artificial intelligence in their real estate strategies. Lastly, adopting a strategy to diversify your real estate portfolio can help mitigate risks associated with urban land use changes.
Understanding the Multiple Nuclei Model
The Multiple Nuclei Model changes how we see urban social structure and economic activities. Created by Chauncy Harris and Edward Ullman in 1945, this model suggests that cities grow not around a single central point, but through multiple centers of activity called nuclei. These nuclei operate independently but are connected through factors like transportation networks and economic activities.
Key Ideas of the Multiple Nuclei Model
- Multiple Centers: Unlike earlier models that focused on one main area, the Multiple Nuclei Model says that cities have several places where things happen.
- Specialization: Each nucleus has its own specific purpose, such as housing, business, or industry.
- Independent Growth Patterns: These nuclei develop on their own based on what they need and what they do.
Importance of Specialized Centers in Urban Growth
- Central Business District (CBD): The CBD remains a focal point for commerce and business activities. It houses corporate offices, financial institutions, and retail outlets.
- Industrial Zones: Located away from residential areas to minimize pollution and noise, these zones focus on manufacturing and heavy industry.
- Residential Districts: Varying from high-density apartment complexes to suburban neighborhoods, these areas cater to different socio-economic groups.
Each specialized center plays an important role in shaping the city. For example:
The CBD attracts businesses due to its accessibility and infrastructure. Industrial zones benefit from proximity to transportation routes like highways and railroads. Residential districts evolve based on factors like school quality and amenities.
Different Growth Patterns Among Various Nuclei
The model suggests that each nucleus has its own growth path influenced by specific factors:
- Economic Activities: Industries tend to cluster together for efficiency and resource sharing.
- Social Dynamics: Residential areas may evolve based on cultural or economic similarities among inhabitants.
- Accessibility: Areas with better transportation links grow faster due to ease of movement for people and goods.
These different growth patterns show how complex urban development is. While each nucleus grows on its own, their connections shape the overall structure of the city.
Understanding this model helps us learn how modern cities develop. It guides planners in creating better urban spaces by recognizing the various needs and functions of different parts of the city.
How Market Segmentation Affects Urban Development
In this context, market segmentation becomes a vital tool for real estate agents and urban planners alike. By dividing a broad market into subsets of consumers with common needs or preferences, real estate professionals can better understand demand patterns in different nuclei such as residential districts or commercial zones.
Moreover, platforms like HelloData provide valuable insights into various markets, making it easier for agents to find potential buyers or sellers. With tools that leverage AI for market analysis, real estate professionals can make more informed decisions about property investments in specific urban areas.
This combination of understanding urban growth patterns through models like the Multiple Nuclei Model and utilizing advanced market segmentation strategies can significantly enhance the
Influencing Factors on Urban Growth in Modern Cities
Urban growth in modern cities is driven by various factors that shape the formation and expansion of nuclei.
1. Transportation Accessibility
Efficient transport networks, including highways, railways, and public transit systems, enable the development of multiple nuclei by connecting different parts of the city. Areas with better transportation links tend to attract more businesses and residents, fostering independent growth centers.
2. Social and Economic Groups
Diverse demographic segments create demand for specialized services and amenities, leading to the establishment of distinct residential districts, commercial hubs, and cultural centers. For instance, high-income neighborhoods may develop around luxury shopping areas, while industrial zones might emerge near lower-income housing due to affordability.
3. Decentralization of Population
As cities expand, populations move away from congested central areas to less densely populated suburbs. This shift encourages the formation of new nuclei as people seek more space and better living conditions outside the traditional Central Business District (CBD).
Understanding these dynamics helps us grasp what is the multiple nuclei model of cities. This model reflects how modern urban landscapes are shaped by a combination of transportation accessibility, social and economic demographics, and the natural tendency for decentralization. Each nucleus grows independently but remains interconnected through various urban systems.
In this context, real estate platforms like Fotocasa can provide valuable insights into property trends across different urban nuclei. These platforms offer unique tools to improve property listings and maximize visibility in a competitive market. Additionally, understanding what is a proptech company can further enhance our comprehension of how technology is revolutionizing the real estate sector in response to these urban growth patterns.
Case Study: Los Angeles as a Model for Multiple Nuclei
Los Angeles is a prime example of the Multiple Nuclei Model in action. This sprawling urban landscape exemplifies how cities evolve with multiple centers of activity, each serving distinct functions.
Key Centers in Los Angeles
- Central Business District (CBD): The downtown area serves as the financial and commercial core, hosting skyscrapers, corporate offices, and cultural institutions.
- Hollywood: Known globally for its entertainment industry, this district is a hub for film studios, production companies, and media-related businesses.
- Beverly Hills: An affluent residential district, Beverly Hills is synonymous with luxury living and high-end retail.
- Santa Monica: A vibrant seaside community offering recreational activities, tourism attractions, and tech startups within Silicon Beach.
- Long Beach: An essential industrial zone featuring one of the busiest ports in the United States. It plays a crucial role in international trade and logistics.
Each center within Los Angeles operates with relative independence yet contributes to the city’s cohesive structure. Specialized zones like these highlight the principle of independent growth patterns among different nuclei. The diversity of functions across these centers underscores the adaptability and complexity embedded within the Multiple Nuclei Model.
Proptech Innovations in Real Estate: Hello Here SL Case Study
Hello Here SL is leading the way in transforming real estate with its advanced AI technology. By combining large amounts of real estate data and using complex algorithms, Hello Here SL tackles important issues in the property search and matching process.
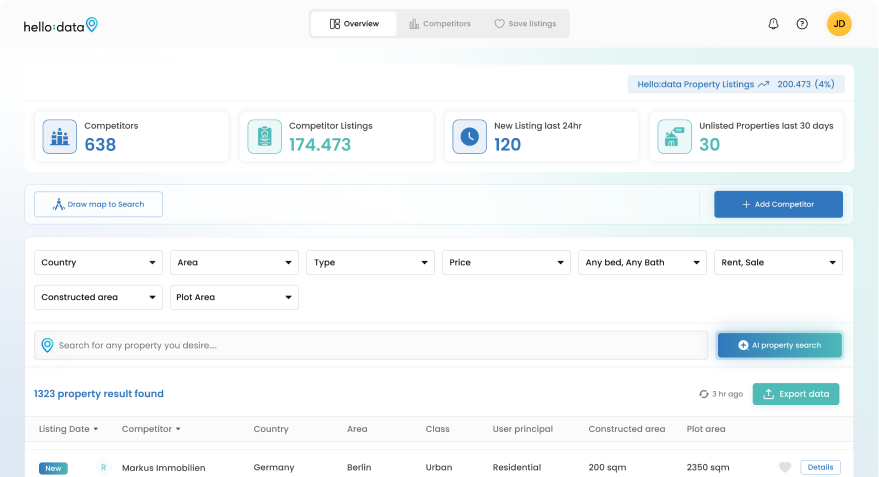
Hello Data Property Tracking
Hello Data Property Tracking stands out by offering:
- Comprehensive Listings: Aggregates an unparalleled volume of real estate data, boasting over 82k properties in Mallorca alone. This is significantly higher than competitors like Idealista.
- AI-Driven Insights: Utilizes artificial intelligence to generate and aggregate data, providing more accurate and efficient property information.
- User-Centric Experience: Focuses on delivering tailored property searches that meet specific user needs, streamlining the decision-making process.
The platform’s ability to surpass traditional platforms such as Zillow showcases its potential to reshape the real estate landscape. For instance, AI Property Search has transformed how renters and landlords navigate the market, making it easier and more efficient.
Navigating Multiple Nuclei with AI
The Multiple Nuclei Model highlights the complexity of modern urban landscapes, where cities grow around multiple centers. For users navigating these intricate environments, Hello Here’s AI-driven platform offers:
- Efficient Navigation: Helps users identify and explore various urban centers based on their preferences (e.g., residential areas, commercial hubs).
- Personalized Matches: Similar to a dating app, it matches users with properties that align with their requirements and lifestyle choices.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By providing detailed insights into different nuclei within cities, users can make informed decisions about where to live or invest.
Moreover, understanding concepts like As Stabilized Value can empower individuals to make informed investment decisions.
Hello Here SL empowers individuals to navigate the complexities of modern cities efficiently. With AI at its core, it transforms how users engage with urban real estate markets.
Benefits Over Traditional Platforms
Unlike conventional platforms like Zillow, Hello Here’s AI-driven approach offers several key benefits:
- Four Times More Listings: Ensures users have access to a broader range of properties.
- Advanced Search Capabilities: Utilizes AI to refine search results based on precise parameters.
- Data Accuracy: Improves the reliability of property information through continual data aggregation and analysis.
By focusing on efficiency and personalization, Hello Here SL sets a new standard for property searches in today’s dynamic urban landscapes.
Hello Here SL’s innovative solutions reflect a deep understanding of urban growth patterns. The integration of AI technology not only enhances property matching efficiency but also helps users make sense of complex city structures following the Multiple Nuclei Model. Additionally, understanding the differences between Black Box vs. Explainable AI (XAI) models can further enhance the user experience by providing more transparency in how AI makes property recommendations.