Introduction
A Full Service Lease in real estate is a comprehensive agreement where the landlord covers all operating expenses associated with the property. This includes property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs. Tenants pay a single, all-inclusive rent amount, simplifying their financial commitments.
Understanding lease types is essential for both tenants and landlords. It sets clear expectations and helps avoid potential disputes. Knowing the differences can lead to better decision-making and optimized investment strategies.
In this article, you will learn:
- The components of a Full Service Lease
- How it compares to other lease types
- The benefits and drawbacks for both tenants and landlords
- Responsibilities under various lease agreements
- Tips for choosing the right lease type for your investment needs
Additionally, with the rise of technology in the real estate sector, platforms like Clickpay are revolutionizing how rent is collected and finances are managed. Furthermore, AI technology is changing rental listings, making it easier for landlords to find suitable tenants.
Moreover, understanding Multifamily housing and the Build-To-Rent (BTR) concept could provide valuable insights for potential investors. Lastly, the innovative AI property search technology offered by platforms like Hello Here is meeting the growing need for effective real estate solutions.
Understanding Full Service Leases
A Full Service Lease, also known as a Full Service Gross Lease, is a comprehensive leasing agreement that bundles various operating expenses into one predictable monthly payment. This structure simplifies budgeting for tenants and provides clarity regarding what is covered. Key components typically included are:
- Property Taxes: Landlords cover property tax obligations, ensuring tenants do not face unexpected tax bills.
- Insurance: The lease usually encompasses property insurance, protecting the building from potential risks.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Regular maintenance responsibilities fall to the landlord, ensuring the property remains in good condition without burdening tenants with repair costs.
- Utilities: Often, utilities like water and electricity are included in this lease structure, adding more predictability to monthly expenses.
In comparison to other lease types, such as Modified Gross or Net Leases, Full Service Leases stand out in several ways:
- Transparent Costs: Tenants benefit from knowing their total costs upfront. Other leases may require additional payments for operating expenses, leading to fluctuating monthly expenses.
- Simplified Management: Property management fees are typically absorbed by landlords. In contrast, net leases often place these responsibilities on tenants, which can complicate financial planning.
This structure appeals to businesses seeking stability and simplicity in their real estate dealings. Understanding these unique features helps both landlords and tenants navigate the leasing landscape effectively.
In today’s evolving real estate market, leveraging technology can further streamline processes such as property searching and enhance overall efficiency. For instance, AI property search tools are revolutionizing the way individuals find suitable properties, making it easier than ever to locate ideal spaces that meet specific needs.
Pros and Cons of Full Service Leases
Advantages of Full Service Lease
For tenants, a Full Service Lease presents several compelling benefits:
- Simplicity in Payment Structure: All expenses are bundled into a single rental payment. This eliminates confusion over separate bills for property taxes, insurance, and maintenance.
- Predictability in Monthly Expenses: With fixed costs, budgeting becomes straightforward. Tenants can anticipate their monthly obligations without worrying about unexpected charges.
This clarity can be particularly advantageous for businesses that need to maintain strict cash flow management. Computer vision technology, for instance, is revolutionizing the real estate sector by providing more accurate property evaluations and data analysis, which can further aid in budgeting and financial planning.
Disadvantages of Full Service Lease
While there are distinct advantages, landlords may face some challenges with this lease type:
- Higher Rental Rates: To cover comprehensive operational costs, landlords often charge higher rents. This could deter potential tenants who might prefer a more cost-effective option.
- Financial Risks: Rising operational costs can pose significant risks. If property expenses increase unexpectedly (like maintenance or insurance), landlords must absorb these costs or adjust rent accordingly, potentially affecting tenant retention.
In such scenarios, understanding market trends through tools like regression analysis can provide valuable insights into pricing strategies and help mitigate financial risks.
Understanding these pros and cons allows both tenants and landlords to make informed decisions when considering a Full Service Lease. Each party must weigh their priorities and financial goals carefully before committing. Additionally, exploring alternative financing options like a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) or adapting to changing interest rates such as those reflected in the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR), could also influence their decision-making process.
Types of Commercial Leases Explained
Understanding the various types of commercial leases is crucial for both landlords and tenants. Each lease type comes with its own terms, responsibilities, and implications for operating expenses management. Here, we break down key lease types while focusing on their unique characteristics.
1. Modified Gross Lease
A Modified Gross Lease strikes a balance between the tenant’s and landlord’s responsibilities. This lease type is designed to provide flexibility while ensuring shared accountability for operating costs.
Key Characteristics:
- Cost Sharing: Under a Modified Gross Lease, tenants typically cover base rent along with a portion of operating expenses such as utilities, property taxes, and insurance.
- Defined Responsibilities: The specific terms outlining which expenses are covered by the landlord versus the tenant are clearly defined in the lease agreement.
Tenant Obligations:
- Operating Expenses: Tenants may be responsible for certain operating expenses like janitorial services or utilities beyond a specified limit. The agreement will detail these obligations.
- Maintenance: Tenants might also need to handle minor repairs or maintenance within their leased space, depending on the terms agreed upon.
Landlord Responsibilities:
- Major Repairs: Landlords generally retain responsibility for major repairs and structural issues, ensuring that the property remains in good condition.
- Insurance Coverage: The landlord is usually accountable for maintaining adequate insurance coverage on the property itself.
This arrangement allows tenants to have more control over certain costs while benefiting from predictable monthly payments. Both parties can negotiate terms based on their needs, leading to a tailored leasing experience.
Comparison with Other Lease Types
Understanding how a Modified Gross Lease stacks up against other common lease structures adds context to its value:
- Net Leases: In contrast to Modified Gross Leases, net leases shift more financial obligations onto tenants. For instance, in a Triple Net Lease, tenants cover property taxes, insurance premiums, and maintenance costs besides the base rent. This can lead to lower base rents but higher overall expenses for tenants.
- Full Service Leases: A Full Service Lease bundles all costs into one comprehensive payment. This arrangement simplifies budgeting but often results in higher rental rates compared to Modified Gross Leases due to the inclusion of all operational costs.
Each lease type has its distinct advantages and challenges. A Modified Gross Lease often appeals to those seeking predictability without relinquishing too much control over operational costs. Understanding these nuances empowers both landlords and tenants to make informed decisions tailored to their financial goals and risk tolerance.
By grasping these different lease structures, you can better navigate the complexities of real estate transactions. This knowledge lays the groundwork for evaluating your options when considering investments or leasing arrangements in commercial real estate.
Furthermore, understanding Rentable Square Footage (RSF) is essential as it represents the total space available for rent, including all usable areas and a proportionate share of common areas.
In addition, exploring strategies like Build-to-Core, which involves constructing new properties with the goal of
2. Net Leases
Net leases are different from both Full Service and Modified Gross Leases because they mainly shift financial responsibilities to tenants. Let’s take a closer look at the various types of net leases:
1. Single Net Lease (N Lease)
In this type of lease, tenants are responsible for paying property taxes in addition to the base rent. On the other hand, landlords are still accountable for maintenance and insurance.
2. Double Net Lease (NN Lease)
With a double net lease, tenants are required to pay both property taxes and insurance on top of the base rent. Maintenance responsibilities typically rest with the landlords.
3. Triple Net Lease (NNN Lease)
Under a triple net lease, tenants take on all operating expenses, which includes property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs. This type of lease often results in a lower base rent but higher overall expenses for tenants.
Key Differences Among Lease Types:
Understanding these differences is important as it clarifies what tenants are responsible for and how operational expenses are managed. Unlike Full Service Leases where all costs are included in one payment, net leases require tenants to handle various costs separately.
Navigating between these lease types is crucial for effective financial planning and investment strategies in real estate. Each lease type offers its own benefits and challenges that can greatly impact the financial outcomes of both landlords and tenants.
For example, understanding LTV in real estate can give insights into how much loan one can take based on the property value.
As the real estate market changes, data analytics play an important role in providing valuable information about property market trends. This is where market segmentation comes into play, allowing real estate professionals to customize their strategies according to specific consumer needs and preferences.
Understanding complex financial terms such as pari passu vs pro rata can also have a significant impact on investment decisions. Lastly, being aware of conditions like warm shell, which provides essential infrastructure while allowing customization, can influence leasing decisions as well.
Responsibilities Under Different Lease Types
1. Responsibilities Under a Full Service Lease
Understanding the responsibilities that come with a Full Service Lease is crucial for both landlords and tenants. This lease type combines multiple costs into one package, providing clarity on what is included in the rental payment. Here’s a closer look at the specific duties typically assigned to landlords under a Full Service Lease agreement:
Property Maintenance and Repairs
Landlords are responsible for maintaining the property in good condition. This includes:
- Routine inspections to ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
- Prompt repairs of any issues that arise, from plumbing leaks to electrical problems.
- Upkeep of common areas, ensuring they remain clean and functional.
Real Estate Taxes
One of the hallmark features of a Full Service Lease is that landlords cover real estate taxes. Tenants benefit from this arrangement as it allows for predictable monthly expenses without unexpected tax bills impacting their budgets.
Insurance Coverage
Landlords must provide insurance coverage for the property. This includes:
- Liability insurance to protect against claims arising from injuries or accidents on the premises.
- Property insurance to cover damage to the structure itself.
Utilities Management
In many cases, landlords are also responsible for managing utilities that service the building. This can encompass:
- Water, gas, and electricity costs associated with common areas.
- Heating and cooling systems maintenance to ensure comfort throughout the property.
Building Property Management
Effective management of the property is paramount. Landlords often need to:
- Hire property management companies if they don’t manage the site directly.
- Handle tenant relations, including addressing complaints and resolving conflicts.
The responsibilities outlined above create a comprehensive framework that supports tenants while allowing them to focus on their business operations without worrying about ancillary costs. Clarity in these responsibilities fosters a positive landlord-tenant relationship, essential for long-term stability and success.
By contrast, other lease types such as Modified Gross or Net Leases allocate varying degrees of responsibility between landlords and tenants. These differences can significantly impact financial planning for both parties. Understanding these nuances helps inform decisions regarding lease agreements and expectations.
With clarity on what constitutes landlord responsibilities under a Full Service Lease, it becomes easier to navigate potential pitfalls in leasing arrangements. Each lease type offers distinct advantages depending on individual needs and circumstances within commercial real estate. Exploring these diverse obligations not only enhances knowledge but empowers informed decision-making for all stakeholders involved in real estate transactions.
Additionally, understanding concepts like Gain to Lease can provide valuable insights for property owners about potential rent increases based on market trends. Moreover, employing tools like a Lease Rent Optimizer can assist landlords in maximizing their rental income efficiently.
On another note, when dealing with complex legal documents related to leasing, having access to lease abstracts can simplify real estate transactions significantly by summarizing critical lease details into easily digestible information.
Furthermore, understanding the income approach in real estate appraisal can enhance valuation skills for property owners seeking accurate assessments of their assets’ worth over time.
2. Responsibilities Under Other Lease Types
Understanding landlord responsibilities and tenant obligations is crucial when navigating different lease agreements. Each lease type delineates specific duties for both parties, impacting financial and operational aspects of property management.
Modified Gross Lease
- Landlord Responsibilities: A blend of Full Service and Net Leases, landlords typically cover base operating expenses like:
- Property taxes
- Insurance premiums
- Tenant Obligations: Tenants handle utility costs and may share additional expenses, depending on the lease terms.
Net Leases
- Single Net Lease:
- Landlord Duties: Responsible for property management and maintenance.
- Tenant Responsibilities: Covers utilities plus a portion of real estate taxes.
- Absolute Net Lease:
- Landlord Role: Minimal responsibility; often only the structure is managed.
- Tenant’s Burden: Assumes all costs, including maintenance, repairs, and property taxes.
Comparison of Lease Terms
Understanding these distinctions clarifies financial expectations. A Full Service Lease offers comprehensive coverage, reducing surprise expenses for tenants. Conversely, Modified Gross and Net Leases can shift more financial risk to tenants. Awareness of these responsibilities enhances decision-making in leasing arrangements.
In situations where selling the property becomes necessary, understanding the cheapest way to sell a house can be beneficial. This knowledge can aid in making informed decisions that align with the financial responsibilities outlined in different lease agreements.
Choosing the Right Lease Type for Investment
Selecting the right lease type is crucial for successful real estate investment. This decision can significantly impact your financial outcomes and operational efficiency. Here are key factors to consider:
1. Risk Tolerance
Understanding how much risk you are willing to take is vital. Different lease types come with varying levels of financial responsibility and potential liabilities. A Full Service Lease might offer predictable expenses, beneficial for conservative investors focusing on stability. In contrast, net leases could attract those willing to manage variable costs for potentially higher returns.
2. Financial Goals
Align your lease type with your investment objectives. Short-term gains may favor different structures compared to long-term asset growth. Evaluate how each lease type will support your broader financial strategy, including cash flow needs and capital appreciation.
Evaluating Property Expenses
Conducting a thorough property expenses analysis is essential before entering a commercial lease agreement. Identify all potential costs associated with different lease types:
- Base Rent: Understand the initial rent and how it compares among lease types.
- Operating Expenses: For Full Service Leases, these costs are typically bundled into the rent, covering property taxes, insurance, maintenance, and utilities. This simplicity allows for easier budgeting.
- Variable Costs: In net leases, expenses such as property taxes or maintenance fees fall on tenants, which can lead to unpredictable monthly payments.
Understanding total cost implications ensures that you choose a lease structure that aligns with your financial capabilities and investment strategy.
Importance of Understanding Total Cost Implications
Before signing a lease agreement, evaluate:
- Long-term Financial Impact: Beyond immediate costs, consider how each type affects long-term profitability. A Full Service Lease may seem more expensive upfront but can mitigate unexpected expenses over time.
- Market Conditions: Analyze current market trends affecting rental rates and operational costs in your target area. This knowledge helps anticipate future expenses and aids in making informed decisions.
- Flexibility Needs: Different lease structures offer varying levels of flexibility regarding term lengths and renewal options. Consider how each option fits within your investment timeline.
In essence, choosing the appropriate lease type involves balancing risk tolerance with financial goals while conducting a detailed analysis of property expenses.
Leveraging Location Quotient in Your Investment Strategy
An often-overlooked aspect of real estate investment is the Location Quotient (LQ). This powerful metric measures the concentration of a particular industry within a specific region compared to a broader benchmark. Understanding and leveraging LQ can significantly boost your property investment strategy by identifying high-potential areas for investment.
The Significance of Breakeven Occupancy
Another critical metric in real estate investment is Breakeven occupancy, which represents the minimum occupancy level required for a property to cover its operating expenses and debt service without incurring losses. This metric should be considered when evaluating potential properties and setting rental rates.
Understanding Liquidity in Real Estate
Furthermore, it’s essential to grasp the concept of liquidity in real estate, which
How Technology is Changing Leasing Processes
Technology is changing the real estate industry, especially when it comes to leasing. With the rise of Proptech and AI in real estate, there are now innovative solutions that make the leasing experience easier and better for both landlords and tenants.
How Technology is Making Leasing Easier
Here are some ways technology is simplifying leasing processes:
- Better Communication: Instant messaging tools and apps streamline communication between tenants and landlords, ensuring quick responses to inquiries.
- Digital Document Management: Electronic signatures and cloud storage allow for efficient management of lease agreements, reducing paperwork and administrative burdens.
- Data-Driven Insights: AI algorithms analyze market trends, helping landlords set competitive rental rates while providing tenants with accurate property evaluations.
Hello Here SL is leading the way in this technological revolution. Their AI-driven real estate app integrates a wealth of data to transform how leasing transactions are conducted.
Future Trends in Property Management and Leasing
As technology continues to evolve, several trends are emerging:
- Increased Automation: Expect more automated processes in property management, such as rent collection reminders and maintenance scheduling.
- AI-Powered Matching Systems: Platforms like Hello Here will refine property matching, connecting tenants with their ideal spaces based on preferences and needs. Their AI property search feature is a prime example of this trend.
- Virtual Tours and Augmented Reality: Prospective tenants can explore properties remotely, enhancing their decision-making process without needing physical visits.
Hello Here: A Game Changer in Leasing Experience
Hello Here is not just another real estate app; it’s a game changer. Its approach leverages advanced technology to provide value-added services that streamline leasing processes effectively. Key features include:
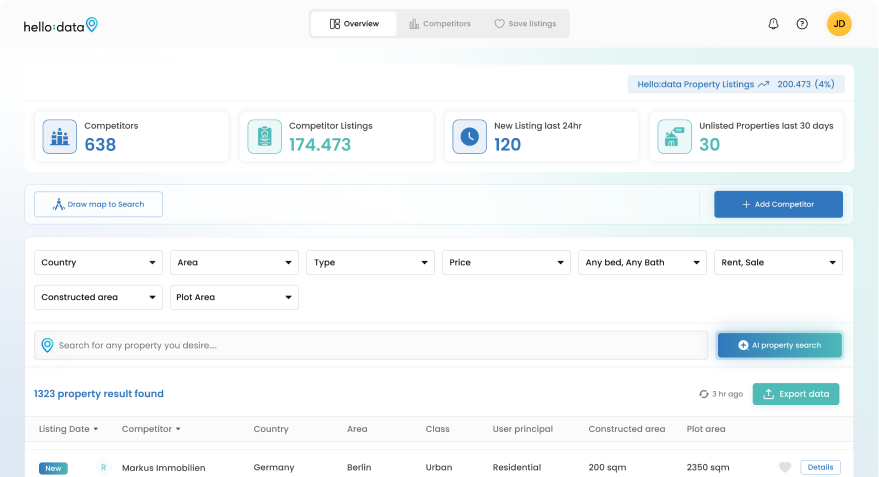
- Hello Data Property Tracking: This B2B tool aggregates real estate data from various sources, surpassing competitors by offering four times more listings. It empowers landlords with comprehensive insights into market dynamics.
- AI Property Matching App (B2C): Similar to dating apps, this consumer-facing solution matches users with properties tailored to their criteria. The integration of AI ensures that suggestions are relevant and timely.
The founders of Hello Here SL—Stephen Nickel and Brahim Zeqiraj—bring expertise from diverse backgrounds. Their vision addresses the gap in targeted property searches, aiming to revolutionize the global real estate market through unmatched efficiency.
Conclusion
Embracing technology like Hello Here’s offerings can significantly influence the leasing process’s success. By leveraging AI-driven solutions, both landlords and tenants can benefit from enhanced experiences that promote informed decision-making. The future of leasing is bright, powered by innovation that transforms how we engage with real estate. For instance, understanding concepts like lender inspections or lockout periods in commercial mortgages can help stakeholders navigate the complexities of real estate finance more effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding what a Full Service Lease in Real Estate entails is crucial for both tenants and landlords. This lease type encompasses comprehensive coverage, including property taxes, maintenance, and insurance costs. By recognizing these components, stakeholders can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and operational needs. The comparison with other lease types reveals the unique features of Full Service Leases, highlighting their predictability and simplicity in payment structures. As we delve deeper into the responsibilities under various lease types, it becomes clear that choosing the right option is vital for maximizing investment potential.